摘要
随着汽车保有量的增加,交通拥堵和交通事故发生率不断升高,作为解决此问题的重要手段,无人驾驶汽车的研究日益迫切。
无人驾驶汽车在复杂交通环境中行驶时会不可避免地与其他交通参与者如汽车、行人和自行车等产生交互,在交互过程中必须避开所有潜在碰撞以保证行驶安全。为了完成此任务,首先需要无人驾驶汽车能够准确地检测并跟踪动态障碍物,估计其运动状态;其次,不同种类的动态障碍物具有不同的运动特性,为提高避撞行为的合理性,需要识别出动态障碍物的种类以便无人驾驶汽车执行更加合理的避撞行为;最后为了避开与动态障碍物之间的潜在碰撞,要求无人驾驶汽车能够准确预测出动态障碍物的运动轨迹,尤其是运动速度较快的动态车辆。
但现有的基于单一轮廓特征的方法在动态障碍物检测跟踪过程中的准确率和速度较低,无法满足动态障碍物避撞安全性的要求,基于轮廓特征和运动状态的动态障碍物识别算法的准确率较低且识别范围较小,无法满足无人驾驶汽车避撞合理性的要求,动态车辆行驶轨迹由很多因素决定,现有的基于动态车辆实时运动状态的轨迹预测方法误差较大,不满足无人驾驶汽车避撞准确性的要求。
针对以上问题,本文提出了基于多特征融合的动态障碍物检测跟踪方法、基于时空特征向量的动态障碍物识别方法和基于驾驶行为意图检测的动态车辆轨迹预测方法,从而实现更加安全、合理和准确的动态障碍物避撞,主要研究内容如下:
1)动态障碍物的检测跟踪:为了提高动态障碍物检测跟踪的准确性与速度,提出了一种基于多特征融合的动态障碍物检测跟踪方法。首先分别从三维激光雷达获得的数据和多层激光雷达获得的数据中提取障碍物的轮廓特征和激光脉冲反射强度特征,接着融合提取的特征并对动态障碍物进行建模,通过构建相似度矩阵完成动态障碍物的匹配跟踪并利用建立的障碍物模型完成动态障碍物的运动状态估计,为动态障碍物识别和动态车辆轨迹预测提供障碍物运动状态信息。
2)动态障碍物的识别:不同类型的动态障碍物具有不同的运动特性且需要不同的避撞策略,为了使无人驾驶汽车能够更加合理地选择避撞行为,本文提出了一种基于时空特征向量的无人驾驶汽车动态障碍物识别方法。首先结合障碍物空间维度上的几何轮廓特征、时间维度上的Zernike不变矩特征和无人驾驶汽车的位姿信息构建时空特征向量,在此基础上使用AdaBoost算法构建动态障碍物分类器,最后使用分类器识别动态障碍物,为避撞行为决策提供障碍物类别信息。
3)动态车辆轨迹预测:在动态障碍物识别的基础上,针对其中动态车辆轨迹预测不准确的问题,提出了基于驾驶行为意图检测的轨迹预测方法。首先,利用高斯混合模型从车辆驾驶行为数据和道路结构信息中学习驾驶行为模式并用于检测动态车辆的驾驶行为意图,接着根据驾驶行为意图检测结果计算动态车辆的长期理想轨迹,并结合运动模型预测动态车辆的行驶轨迹,为准确的碰撞检测和避撞奠定基础。
最后,通过在城区交通环境中的实车实验验证了上述技术的可靠性与稳定性,极大地提升了动态障碍物检测跟踪的准确性与速度,提高了动态障碍物的识别准确率和动态车辆的轨迹预测精度并扩展了动态障碍物识别距离范围。
关键词:无人驾驶汽车;动态障碍物;避撞;检测跟踪;识别;时空特征向量;驾驶行为意图检测;轨迹预测
ABSTRACT
With the increase of car ownership, the incidence of tral}ic congestion and traffic accidents is increasing. As an important means to solve this problem, the research of autonomous vehicles is becoming more and more urgent.
It is inevitable for autonomous vehicle to interact with other traffic participants, such as cars, pedestrians and bicycles, when driving in complex traffic environments.
The dynamic obstacle collision avoidance system must avoid all potential collisions in the interactive process to ensure driving safety. To accomplish this task, firstly, the dynamic obstacles must be detected and tracked precisely and their moving states should be estimated simultaneously. Secondly, different kinds of dynamic obstacles have different movement characteristics. It is necessary to identify the types of detected dynamic obstacles so that the decision system can generate more reasonable obstacle avoidance behavior. Finally, in order to avoid the potential collision between the dynamic obstacle and the autonomous vehicle, it is required to predict the trajectory of detected dynamic obstacles, especially for the fast moving dynamic vehicles. Whereas the accuracy and speed of the existing outline feature based dynamic obstacle detection and tracking method needs to be improved. The accuracy and recognition range of the existing dynamic obstacle recognition algorithm, which is based on contour feature and moving state, needs to be improved. For existing trajectory prediction methods that are based on the real-time motion state, it is difficult to obtain accurate trajectories of detected vehicles.
In view of the above problems, a mufti-feature fusion based dynamic obstacle detection and tracking method, a spatio-temporal feature vector based dynamic obstacle identification method and a driving-intent estimation based trajectory prediction method are proposed in this dissertation to achieve safer, more reasonable and accurate dynamic obstacle avoidance. The main research contents are as follows:
1) Detection and tracking of dynamic obstacles: In order to improve the accuracy and speed of dynamic obstacle detection, a mufti-feature fusion based dynamic obstacle detection and tracking method is proposed. The contour feature and laser pulse reflection of obstacles are extracted from the 3D laser point cloud data and the two-dimensional laser point set data respectively. The extracted features are fused and used to model the detected obstacles. Then, the matching of dynamic obstacles is completed and the motion state is estimated which is used to support dynamic vehicle trajectory prediction.
2) Dynamic obstacle recognition: Different types of dynamic obstacles have different motion characteristics and require different obstacle avoidance strategy. In order to make the autonomous vehicle more intelligent when choosing obstacle avoidance behavior, a spatio-temporal feature vector based dynamic obstacle identification method is proposed. Firstly, the geometric contours of dynamic obstacle in multi-frame data, the real-time Zernike invariant moments of dynamic obstacle and the relative position of autonomous vehicle are used to construct the spatio-temporal feature vector. Then the AdaBoost algorithm is used to train the classifier which is used to identify the detected dynamic obstacles.
3) Dynamic vehicle trajectory prediction: Based on the identification of detected dynamic obstacles, aiming at the problem of inaccurate prediction of dynamic vehicle trajectory which threatens driving safety, an intent-estimation based trajectory prediction and collision avoidance method is proposed. Firstly, the driving behavior pattern is learned from the vehicle driving behavior data and the road structure information by using the Gaussian mixture model which is used to detect the driving behavior intention of the detected dynamic vehicle. Then, the long-term ideal trajectory of the dynamic vehicle is calculated according to the driving behavior intention.
Combined with the long-term ideal trajectory, constant acceleration and yaw rate velocity motion model is used to predict the driving trajectory of dynamic vehicles, which lay the foundation for accurate collision detection.
Finally, the reliability and stability of the above technologies are verified by the actual vehicle experiment in the urban traffic environments. The accuracy and speed of the dynamic obstacle detection and tracking are greatly improved as well as the accuracy of the dynamic obstacle recognition and the trajectory prediction of dynamic vehicles. Besides, the range of dynamic obstacle identification distance is extended.
Key Words: autonomous vehicle, dynamic obstacle, collision avoidance, detection and tracking, identification, spatial-temporal feature vector, driving intent estimation,trajectory prediction
交通事故每年造成约125万人死亡以及数千亿美元的经济损失,如果不采取行动,预计到2030年会成为世界第七大死亡原因(世界卫生组织,2015),而交通事故发生的最主要原因是驾驶员的操作失误。人类感知和控制能力的局限使得驾驶员在面对突发状况时无法及时做出合理的决策,此外驾驶疲劳也是造成交通事故的重要原因,随着人工智能、计算机技术以及芯片技术的发展,无人驾驶汽车的使用成为了减少交通事故的最重要手段之一。
从1970年代起,无人驾驶汽车的研究进入快速发展阶段,美国、欧洲和日本就相继启动了无人驾驶汽车研究项目,对无人驾驶的基础性技术进行研究。上世纪80年代,美国和欧洲相继启动了自主陆地车辆项目((Thorpe et al. 1988)和普罗米修斯项目,接着日本在90年代启动了高速公路高级辅助巡航系统研发计划,在无人驾驶汽车发展史上美国国防部先进研究项目局(Defense AdvancedResearch Projects Agency, DARPA)举办的三次无人驾驶汽车挑战赛具有里程碑意义,比赛结果不但证明了无人驾驶汽车的可行性,同时极大的推动了无人驾驶技术的发展。
虽然无人驾驶汽车技术在过去10年取得了长足进步,部分无人驾驶汽车已经进入测试阶段(State of California, 2017 ),但由于真实的交通环境包含多种类型的交通参与者,无人驾驶汽车在行驶时会不可避免的与其他交通参与者产生交互,为了保证行驶安全性,无人驾驶汽车必须避开所有的潜在碰撞,为了完成这个目标,在具备高速高精度轨迹跟随能力的前提下,无人驾驶汽车的动态障碍物避撞系统还需要解决以下三个问题:首先需要自动驾驶车辆能够准确的检测出环境中的动态障碍物并对其进行跟踪,为障碍物识别和轨迹预测提供障碍物的运动状态信息,但现有的基于单一轮廓特征的方法在检测跟踪过程中的准确率和速度较低,无法同时满足无人驾驶汽车安全行驶的要求;其次需要无人驾驶汽车能够识别出动态障碍物的类型,为避撞行为决策提供信息支撑,但现有的基于轮廓特征和运动状态的动态障碍物识别算法的准确率较低且其识别范围较小,无法满足无人驾驶汽车避撞合理性的要求;最后要求无人驾驶汽车能够准确预测出环境中动态车辆的行驶轨迹以准确执行避撞行为,但动态车辆行驶轨迹由很多因素决定,现有的基于动态车辆实时运动状态的轨迹预测方法无法预测出准确的行驶轨迹。
综上所述,无人驾驶汽车的研究能够极大提高交通安全,而动态障碍物检测跟踪、动态障碍物识别和动态车辆轨迹预测是无人驾驶汽车动态障碍物避撞涉及到的三项关键技术,不解决这些关键技术中存在的问题无人驾驶汽车无法在真实交通环境中投入使用。
自动驾驶汽车的概念的形成可以追溯到1920年代(Geddes N B, etal. , 2012),设计师N二二n Bel在1940年设计的“未来展台”中首先提出了无人驾驶汽车的完整概念,即一种只需要简单的设定就可以自主行驶并完成任务的新型汽车。在1950年代,美国的部分企业和科研机构就己经开展了无人驾驶技术的研究,贝瑞特电子公司研制出世界上第一台自主导航车,能够在设定的轨道中行驶。1980年代,卡内基梅隆大学研制成功了世界上第一辆真正意义上的无人驾驶汽车Navlab-1,但是由于受到软件技术限制,直到1980年代末,行驶速度才能够达到32千米每小时(Thorpe C, et a1.,1988)。美国国防部高级研究计划局与美国陆军联合发起了自主地面车辆研究计划(Autonomous Land VehicleProjec七),建造了一辆能以较低速度自主行驶的八轮汽车,不过该自主车只能在有限的结构化环境中行驶,无法应对颠簸路况。1990年代,卡内基梅隆大学在Navlab-1基础上研制出了Navlab系列无人驾驶汽车,其中Navlab-5能够进行复杂地形下的长距离高速度的自主行驶,完成了长达上万公里的行驶实验。为了评估无人驾驶技术评估无人驾驶汽车在军事领域应用的可行性,美国国防部高级研究计划局分别在2004年、2005年以及2007年针对越野环境无人驾驶与城区环境无人驾驶举行了三场无人驾驶汽车挑战赛,这三场比赛的参赛队伍代表了当时无人驾驶技术的最高水平。
2004年的DARPA Ground Challenge中,比赛中行驶最远的Carnegie-Mellon大学的Sandstorm无人驾驶汽车也只完成了11.78千米。2005年的第二届GroundChallenge中,最终有5辆无人驾驶汽车完成了212公里的沙漠赛程,其中斯坦福大学的Stanley无人车获得了冠军(Thrun S , et a1.,2004 ) 0 2007年的UrbanChallenge中,卡内基梅隆大学的BOSS无人车用时4小时10分完成了96千米的赛程获得冠军(Urmson C, et al., 2008 ),图1.I展示了DARPA无人车比赛中表现优异的无人驾驶汽车。这三次比赛极大的推动了无人驾驶汽车软硬件的发展,使无人驾驶汽车技术的可行性得到了政府和企业的认可,催生了三维激光雷达等传感器在自动驾驶汽车上的应用,也开启了无人驾驶汽车商业化的序幕。
基于多特征融合动态障碍物检测跟踪方法:
典型箱行驶轨迹
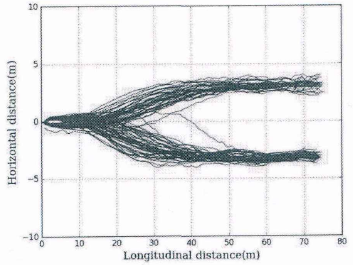
换道轨迹
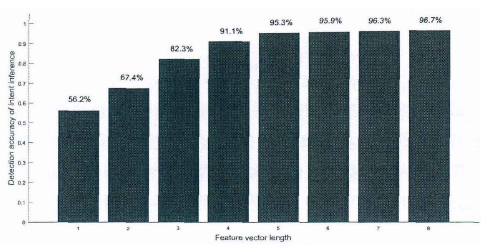
向量长度与准确率的关系
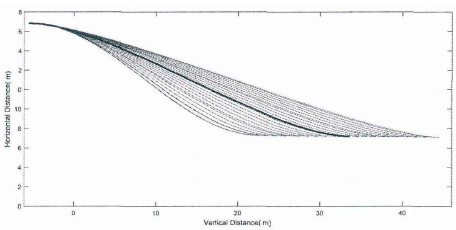
备选轨迹蔟(红色虚线)和最终选择的理想轨迹(蓝色实线)
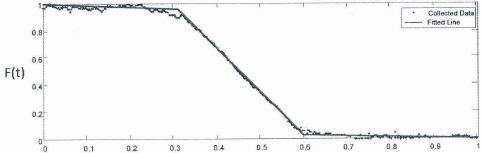
长期理想轨迹影响因子曲线
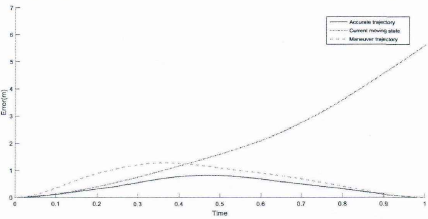
轨迹预测误差
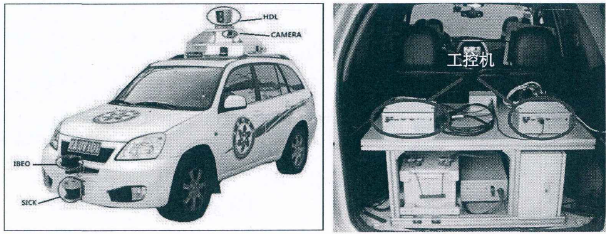
智能先锋2号

典型实验场景
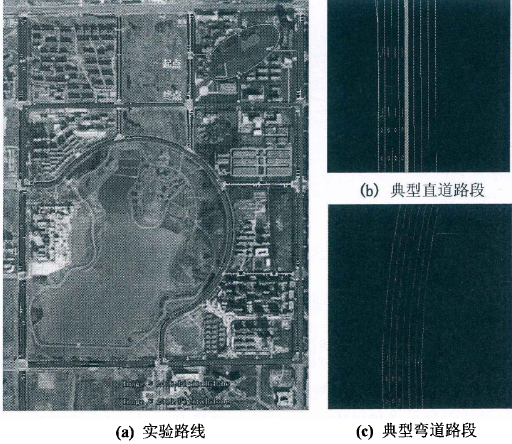

实验路线和环境
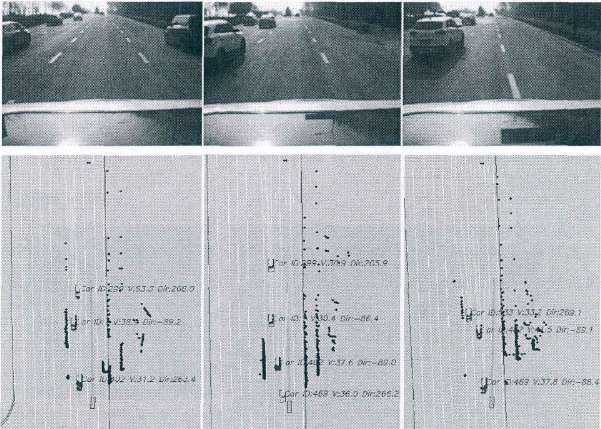

较大交通流的直道驾驶场景避撞过程
目录
第1章 绪论
1.1 课题背景及意义
1.2 国内外无人驾驶汽车研究现状及分析
1.3 动态障碍物检测跟踪方法研究现状与分析
1.4 动态障碍物识别方法研究现状与分析
1.5 动态车辆轨迹预测与避撞方法研究现状与分析
1.6 研究基础与存在的问题
1.7 本文创新点与研究内容组织架构
1.7.1 本文创新点
1.7.2 本文主要研究内容与结构安排
第2章 动态障碍物避撞系统设计
2.1 无人驾驶汽车平台体系结构
2.1.1 感知系统
2.1.2 决策系统
2.1.3 控制执行系统二
2.2 无人驾驶汽车动态障碍物避撞关键问题
2.2.1 动态障碍物检测跟踪的关键问题
2.2.2 动态障碍物识别的关键问题
2.2.3 动态车辆轨迹预测的关键问题
2.3 动态障碍物避撞方法分析
2.3.1 设计要求
2.3.2 解决方案
2.4 本章小结
第3章 基于多特征融合的动态障碍物检测跟踪
3.1 障碍物特征融合与建模
3.1.1 多层激光雷达数据特征提取
3.1.2 维激光雷达数据特征提取
3.1.3 动态障碍物特征融合与建模
3.2 动态障碍物检测跟踪
3.2.1 动态障碍物匹配.
3.2.2 动态障碍物的运动状态估计
3.3 实验结果
3.4 本章小结
第4章 基于时空特征向量的动态障碍物识别
4.1 时空特征向量构建
4.1.1 空间维度特征
4.1.2 时间维度特征
4.2 基于AdaBoost算法的动态障碍物识别
4.2.1 Adaboost算法理论基础...
4.2.2 分类器构造
4.3 实验结果
4.4 本章小结
第5章 基于驾驶行为意图检测的动态车辆轨迹预测与避撞
5.1 基于混合高斯模型的驾驶行为意图检测
5.1.1 基于动态车辆运动特征和道路结构的特征向量构建
5.1.2 基于混合高斯模型的驾驶行为意图检测
5.2 基于驾驶行为意图的轨迹预测与避撞
5.2.1 动态车辆轨迹预测
5.2.2 避撞方法
5.3 实验结果
5.4 本章小结
第6章 实验与讨论
6.1 实验平台
6.2 实验场景
6.3 实验设计
6.4 实验结果分析
6.4.1 交通流较大的直道场景
6.4.2 曲率较大的弯曲道路场景
6.4.4 包含多种交通参与者的场景
6.4.3 整体测试结果分析二
6.5 本章小结
第7章 总结与展望
7.1 总结
7.2 展望
参考文献
致谢
(如您需要查看本篇毕业设计全文,请您联系客服索取)